LMS WITH USER ROLES AND GROUP MANAGEMENT
User roles and group management within an LMS helps to define your organization’s structure and hierarchy. Abara LMS helps you differentiate between learners, administrators, instructors, and other users based on roles and responsibilities.


MASTER ADMINISTRATOR
Abara LMS allows one user the ability to manage the entire system including the system setup and configuration, permissions, and the ability to add other sub- administrators, etc. Such users are called Master Administrators. Master Administrators are users with the highest level of rights over the LMS’ set up, administration, and its operations.

SUB-ADMINISTRATOR
A Master Administrator defines the Sub-Administrator role on the LMS. The Master Administrator also delegates administrative tasks to the Sub-Administrator. Master Administrators solely delegate tasks, authority, and administrative abilities to the Sub-Administrator.

POWER USER
On Abara’s hierarchy chart, Power Users and Sub-Administrators are the same. The Master Administrator sub-delegates the same authority to both roles. However, Power Users can access the learner side as well, making that the only difference. As a result, Power Users can enroll in a course as an actual learner and manage the LMS as a Sub-Administrator as well.
The Master Administrator oversees the defining of roles—the actions that Sub-Administrators and Power Users can take—like assigning learners, adding courses, etc. Each role has their own set of rights.

LEARNER
Learners are the core users of an LMS. In Abara’s case, learners are your employees who use the platform to train and develop their skills.
Abara allows your learners to consult with experts and interact with other administrative roles present within the LMS as well.
Also, Abara is a balanced learning management system. Its optimized dashboard simplifies your learner’s journey using widgets, progress reports, calendars, and notifications to indicate certificate updates.

LINE MANAGER
Line Managers are heads or executives in charge of managing teams.
Like their team members, Line Managers also need to train and develop their skills. However, as an executive overlooking the performance of their team members, Line Managers are offered additional rights on the Abara platform. Line Managers can oversee the training initiatives and progress of their team members.
Line Managers also need to ensure learners in their teams have the time and space to complete courses while also suggesting and approving their course enrolment requests.

INSTRUCTOR
Instructors can manage attendance, conduct live classes, approve course requests, evaluate assessments, and check reports.
Learners or Line Managers can additionally act as instructors. Instructors can also mark attendance of learners, book live classes, approve course requests, evaluate assessments, check reports, and more.

EXTERNAL INSTRUCTOR
An External Instructor is like a Learner, Line Manager, or Instructor albeit with fewer rights.
The difference between an internal employee with Instructor rights vs. an External Instructor is that the latter may not be an employee of your organization. An External Instructor may be a vendor or a contractor with a specific role like conducting training for employees and using the LMS to facilitate training sessions—ILT and vILT—based on the given rights.

USER ROLES AND GROUP MANAGEMENT

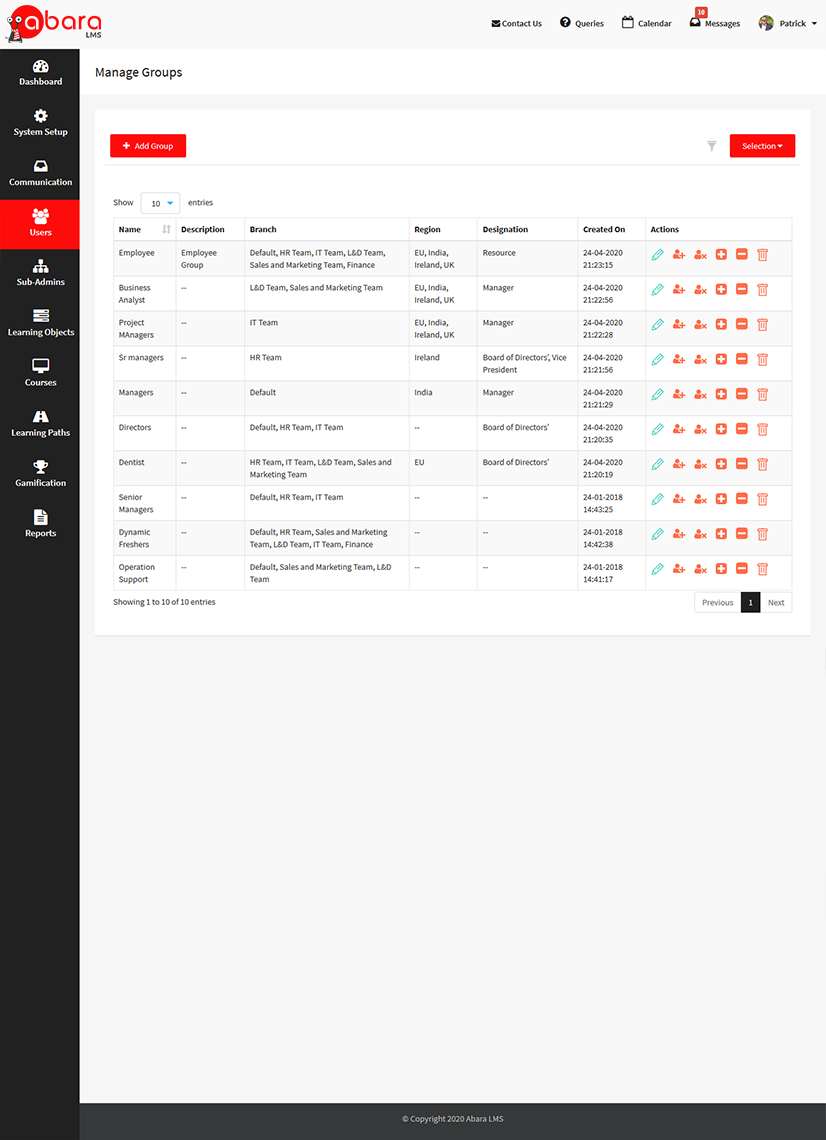
ORGANIZING USERS AND GROUPS ON ABARA LMS
Abara allows learners and managers to organize or segment user data in multiple methods:
Branch: This is the default way to segment users within the system. For a small organization, this may be enough. Larger organizations may need to combine this with custom fields.
Group: This is another way to easily organize your users within the system for assignment and reporting.
Custom Field: This is a powerful feature to segment and organize the users within the system in any way you want. Administrators have complete flexibility to structure their organization and connect to third-party systems’ meta-data requirements.
Sub-administrator, Line Manager, and Power User roles can be restricted to a branch, a group, and/or a custom field. Reports can also be extracted for each of these users’ meta data types.
Abara LMS’s Customer Success and Onboarding Team will understand the user data structures that your organization needs based on size and will help you to map out the structure within Abara LMS using these three methods.
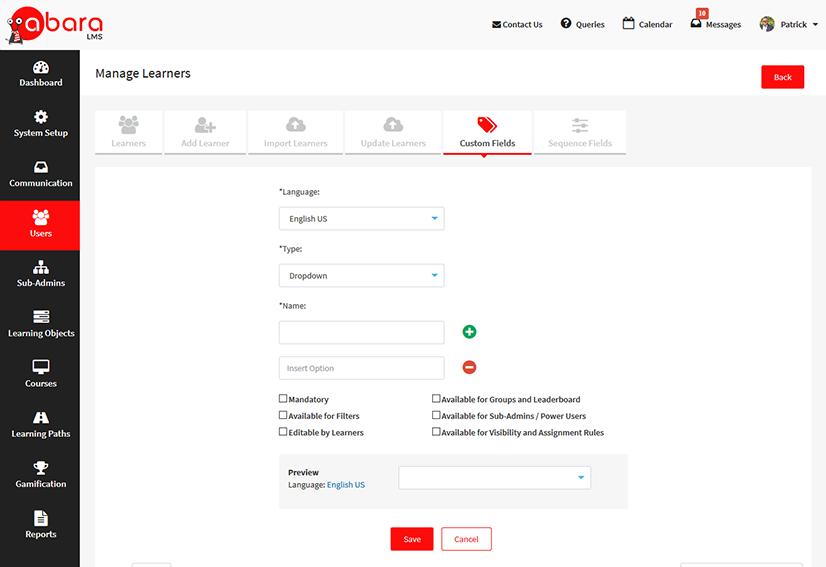
CUSTOM FIELDS
The importance of the custom fields feature is based on its ability to create almost any datatype to organize and structure a user’s meta-data. The datatypes include:
Creation of drop-downs
Text entry
Free text entry
Number
Date
Upload file
Customers appreciate Abara’s custom fields feature for its ability to handle all possible scenarios needed to organize user data. Custom fields can also be used for:
Filtering screens and reports for Administrators, Power Users, Line Managers, etc.
Group management
Leaderboards
Course/learning path visibility rules for learner catalog
Auto-assignment rules


USE CASE FOR BRANCH, GROUPS, AND CUSTOM FIELDS

Abara LMS uses branches, groups, and custom fields for multiple purposes depending on the size and complexity of your organization. Branches and groups may be sufficient for smaller organizations.
Custom fields are a powerful way to organize and segment user data for large enterprise organizations with limitless ability to handle organization structures.
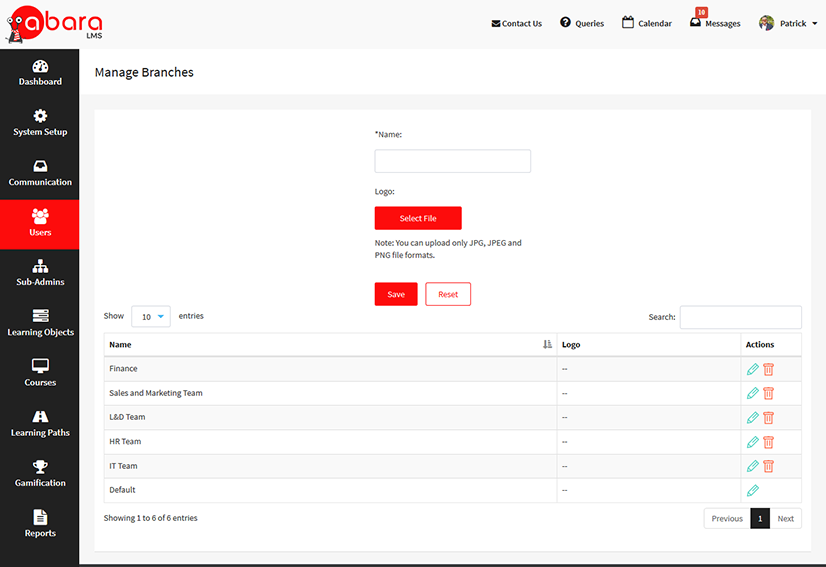

SMALL ORGANIZATION
Branch: This could be used to organize users by departments such as Sales, Marketing, Operations, Customer Service, and Management.
Group: This could be used to organize sales teams by the products/services that they sell/support if a secondary method is required to organize users from within the branches.
Custom Fields: Used to specify the user’s city, address, designation, role, etc.
LARGE ORGANIZATION
Branch: This could be used to organize users by location in case of a large multi-location organization.
Group: This could be used to organize teams within each location by department if a secondary method is required to organize users from within the branches.
Custom Fields: This could be used to specify the user’s city, address, designation, role, etc.

TO KNOW MORE ABOUT ABARA’S LMS WITH USER ROLES AND GROUP MANAGEMENT FEATURES, SCHEDULE A DEMO
TO KNOW MORE ABOUT ABARA’S LMS WITH USER ROLES AND GROUP MANAGEMENT FEATURES, SCHEDULE A DEMO

